The most well-known program or project management methodology is the SCRUM Agile method. Agile methodology offers many benefits over the traditional methods of software development.
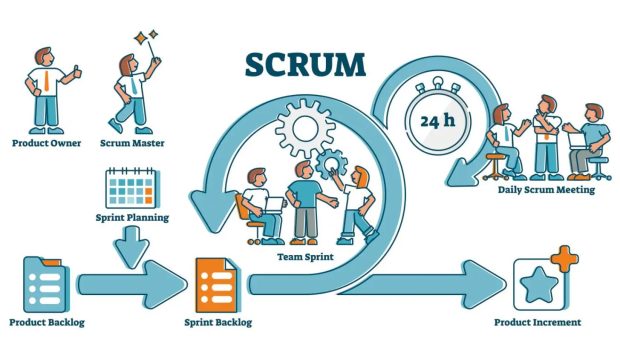
Scrum’s methodology is iterated, incremental (product functionality increases during short cycles called iterations), and uses its terminology for workers. The Scrum Master, the Scrum team, and the product owner comprise the project team, and each member has a different task.
But all of them are the participants of the sprint review.
The product owner manages the review process. The Scrum Master makes sure that everyone understands what the event is about.
Do you know which statement best describes the sprint review?
Yes, it is the most perceptible activity that takes place in Scrum.
Further, Scrum is divided into three phases: pregame, postgame, and game. Although the structure of Scrum is complex, it’s not complicated!
Quick intro: Scrum Methodology
Scrum can be described as a repetitive framework for product and software development. Employees are the team owners, and employees are the players. The game itself is an improvement opportunity. Once the game is over, we can see clearly what is unacceptable and what is working. Scrum methodology can identify and fix deficiencies, and Scrum methodology teaches you how to play the game. A scrum is a tool that helps companies coordinate extensive production processes – especially when there are many “teams.” Control is crucial.
Scrum methodology recognizes that there will always be obstacles in the way of perfection. Therefore, Scrum proposes to introduce Sprints into the process to overcome these obstacles.
Assets of Scrum Methodology:

The benefits are on both sites. The client is happy because they received what they needed and expected. For developers, the benefits of participating in Scrum methodology are more subjective – it might be their motivation and satisfaction of doing the work efficiently.
Now comes the team, the scrum team:
Scrum is made up of:
• Product owner
• Scrum Master
• Developers
The product owner determines the features of the product. He decides which functions are most essential and must be implemented. He represents many others involved in the project. It is often a member of the marketing team or a significant customer.
The Scrum Master oversees the team and ensures that the process aligns with Scrum principles. He is responsible for solving problems, e.g., developers do not have the right software or tools.
Developers are the last part of Scrum’s team, and developers are the ones who create the software. The project developer may have different tasks. However, the Scrum methodology allows for any number of people to be involved in developing software, such as programming, documentation, and projecting.
The scrum project

Sometimes, Scrum team projects are divided into two parts:
• Management – It decides the initial process’s content and timing manages the product’s extension, and influences the backlog, risk, and release content.
• Developers, documenters, and quality control staff make up the development teams. They typically consist of between 3-6 people. Each group has its task and decides what changes must be made to implement items from the backlog, such as before implementing a new function. Sometimes, teams can be broken up into functionality (functionality derived) or system (system derived).
Features:

• Scrum is iterative (that is, the project is realized over successive cycles called sprints or iterations) and incremental (the functionality of each product increases during each iteration by adding new functions).
• The Scrum process can be divided into three phases: pregame (planning and system architecture), game (development sprints), or postgame (closure). Planning and closing phases are well-defined and well-documented processes. On the other hand, the sprint phase processes are unpredicted, uncontrolled, and undefined.
• Scrum is not dependent on external factors such as time, financial and competitive pressure (until the last stage) and is flexible (adapts to changing environmental conditions).
• Scrum is reviewed as often and as frequently as needed.
Professionals adapt Scrum all over the world for its unique features. It reduces their work and makes it easier to get things done. These are the features, you might ask. Let’s find the answers!
1. Sprint Sessions: When planning a project, we often add a time frame. Studies show that we often underestimate the time it takes or overestimates the duration. These approaches can cause problems during a project. In most cases, the executors and planners will have differing mindsets. Therefore, the executors may not be able to implement the plan the planners created. Scrum recommends sprint sessions to avoid these obstacles. This method allows the whole team to be divided into smaller groups of 3-9 people, working together towards a common goal for at least a week. They discuss the progress made in the project and decide what needs to be done before the next sprint session. Because the planners are the executors, these sessions are more successful.
The plan is also regularly updated, and the team is motivated.
2. Display progress: Large-scale projects often involve many teams in different areas of the project. Communication between these teams can prove difficult in such situations. It can also be an energy booster if each group can see the progress of other teams. Scrum recommends that every team has a chart to see all of their work. This can encourage slow workers to work faster and encourage active workers to keep up their pace.
3. The Burndown Chart: It is a traditional chart/graph that shows the work done by different teams. This is believed to increase employee morale and motivate them to work harder. Scrum recommends a reverse approach. Scrum methodology suggests that a “Burndown” chart be displayed each week. The chart should include the remaining work days and the amount of work pending on the axes. The chart should clearly show how much work remains so that employees can know how long they have to complete the task.
4. Specific Meetings – Corporate meetings are held every day, and these meetings can go on for hours and have little to no impact on the project’s progress. To address this problem, Scrum recommends that daily meetings be held at short intervals. These meetings shouldn’t last more than 10 minutes, and the discussion should not be extended beyond discussing the project and the different plans for achieving the goal. Only three questions should ever be asked and answered.
Conclusion
Scrum’s unique feature is its ability to adapt to changing market conditions. It incorporates these changes into the product development cycle late in the development process. Scrum focuses on adapting quickly to changing environments and incorporating those changes into the product design.
 Jewel Beat
Jewel Beat

